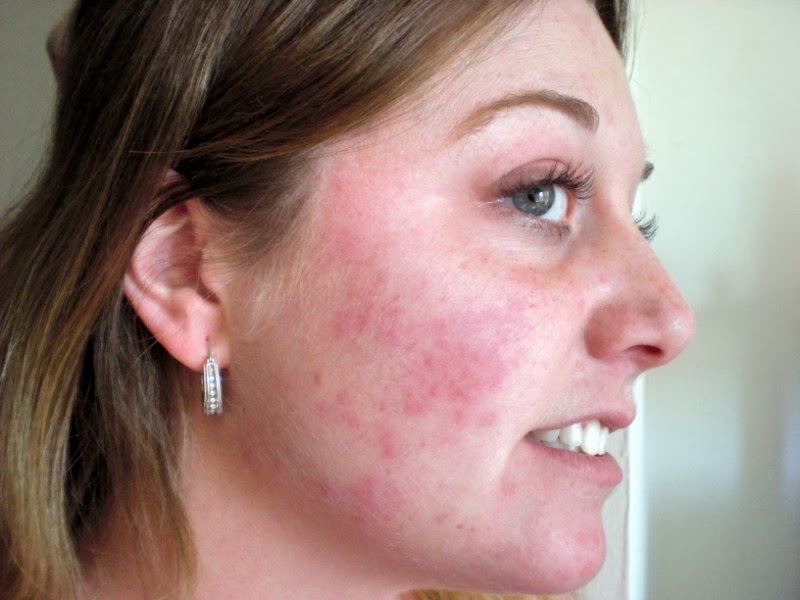
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face is a type of contact dermatitis, which is a skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen. Neosporin is a topical antibiotic ointment that is used to treat minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. It contains three antibiotics: neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin. An allergic reaction to Neosporin can range from mild to severe, and symptoms can include redness, swelling, itching, burning, and blistering. In severe cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can lead to anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
It is important to be aware of the potential for an allergic reaction to Neosporin, especially if you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities. If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin, you should discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention.
There are a number of alternative treatments for minor cuts, scrapes, and burns that do not contain Neosporin. These include other topical antibiotics, such as bacitracin or mupirocin, as well as over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Allergic Reaction to Neosporin on Face
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face is a type of contact dermatitis, which is a skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen. Neosporin is a topical antibiotic ointment that is used to treat minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. It contains three antibiotics: neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin. An allergic reaction to Neosporin can range from mild to severe, and symptoms can include redness, swelling, itching, burning, and blistering. In severe cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can lead to anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, itching, burning, blistering
- Causes: Contact with Neosporin, which contains the antibiotics neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin
- Treatment: Discontinue use of Neosporin and seek medical attention
- Prevention: Avoid contact with Neosporin if you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities
- Alternatives: Other topical antibiotics, such as bacitracin or mupirocin, as well as over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Complications: In severe cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can lead to anaphylaxis
- Diagnosis: Based on symptoms and a history of exposure to Neosporin
- Prognosis: Most people who experience an allergic reaction to Neosporin will recover with treatment
It is important to be aware of the potential for an allergic reaction to Neosporin, especially if you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities. If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin, you should discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention.
Symptoms
Redness, swelling, itching, burning, and blistering are all common symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face. These symptoms are caused by the body's immune system overreacting to the Neosporin, which it perceives as a foreign invader. The immune system releases histamines and other chemicals that cause the blood vessels in the skin to dilate, leading to redness and swelling. The histamines also cause the skin to become itchy and painful, and in some cases, they can cause blisters to form.
It is important to be able to recognize the symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin so that you can discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention if necessary. In most cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin will resolve on its own within a few days. However, in severe cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can lead to anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
If you experience any of the symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin, it is important to discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention. Your doctor will be able to confirm the diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment.
Causes
Neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin are the three antibiotics that are found in Neosporin. These antibiotics work by killing bacteria that can cause infections. However, some people are allergic to these antibiotics, and when they come into contact with Neosporin, they can develop an allergic reaction.
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can range from mild to severe. In mild cases, the reaction may cause redness, swelling, and itching. In severe cases, the reaction can cause blistering, hives, and difficulty breathing. In rare cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can be life-threatening.
It is important to be aware of the potential for an allergic reaction to Neosporin, especially if you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities. If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin, you should discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention.
If you are allergic to Neosporin, there are a number of other topical antibiotics that you can use to treat minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. Your doctor can recommend the best option for you.
1. Treatment
Discontinuing use of Neosporin and seeking medical attention are crucial steps in managing an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face. An allergic reaction to Neosporin can range from mild to severe, and in rare cases, it can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to take immediate action to stop the allergic reaction and prevent further complications.
The first step in treating an allergic reaction to Neosporin is to discontinue use of the product. This will help to stop the exposure to the allergen and allow the skin to begin healing. Once Neosporin has been discontinued, it is important to seek medical attention to confirm the diagnosis and receive appropriate treatment. The doctor may prescribe topical or oral medications to help reduce the inflammation and itching. In severe cases, the doctor may also prescribe epinephrine, which is a medication that can help to open up the airways and prevent anaphylaxis.
It is important to follow the doctor's instructions carefully and to take all medications as directed. It is also important to avoid contact with Neosporin in the future, as even a small amount of exposure can trigger an allergic reaction. By following these steps, you can help to manage your allergic reaction to Neosporin and prevent future complications.
Prevention
If you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities, it is important to avoid contact with Neosporin to prevent an allergic reaction on the face. Neosporin is a topical antibiotic ointment that contains three antibiotics: neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin. Some people are allergic to these antibiotics, and when they come into contact with Neosporin, they can develop an allergic reaction.
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can range from mild to severe. In mild cases, the reaction may cause redness, swelling, and itching. In severe cases, the reaction can cause blistering, hives, and difficulty breathing. In rare cases, an allergic reaction to Neosporin can be life-threatening.
Avoiding contact with Neosporin is the best way to prevent an allergic reaction. If you have a history of allergies or skin sensitivities, it is important to read the labels of all medications and products that you use to make sure that they do not contain Neosporin. You should also avoid contact with Neosporin if you have a known allergy to any of the ingredients in the product.
If you accidentally come into contact with Neosporin and you develop an allergic reaction, it is important to discontinue use of the product and seek medical attention. Your doctor will be able to confirm the diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment.
2. Alternatives
When it comes to treating minor cuts, scrapes, and burns on the face, there are a number of alternatives to Neosporin that can be used to avoid an allergic reaction. Other topical antibiotics, such as bacitracin or mupirocin, are effective at preventing and treating infections, and they are less likely to cause an allergic reaction. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also be used to reduce pain and inflammation associated with minor injuries.
- Bacitracin: Bacitracin is a topical antibiotic that is effective against a wide range of bacteria. It is available in both ointment and cream form, and it is generally well-tolerated. Bacitracin is a good alternative to Neosporin for people who are allergic to neomycin or polymyxin B.
- Mupirocin: Mupirocin is a topical antibiotic that is effective against staph bacteria. It is available in both ointment and cream form, and it is generally well-tolerated. Mupirocin is a good alternative to Neosporin for people who are allergic to neomycin, polymyxin B, or bacitracin.
- Ibuprofen: Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is effective at reducing pain and inflammation. It is available in both oral and topical form. Topical ibuprofen is a good alternative to Neosporin for people who are allergic to neomycin, polymyxin B, or bacitracin, and who are experiencing pain and inflammation associated with a minor injury.
- Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that is effective at reducing pain and fever. It is available in both oral and topical form. Topical acetaminophen is a good alternative to Neosporin for people who are allergic to neomycin, polymyxin B, or bacitracin, and who are experiencing pain associated with a minor injury.
It is important to note that these alternatives are not necessarily more effective than Neosporin. However, they are less likely to cause an allergic reaction, which makes them a good choice for people who are allergic to Neosporin or who have sensitive skin.
3. Complications
Anaphylaxis is a rare but serious allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to an allergen, and it can affect multiple organs in the body. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, throat, and tongue, hives, itching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness. In severe cases, anaphylaxis can lead to unconsciousness and death.
- Risk factors for anaphylaxis: People who are allergic to Neosporin are at risk for developing anaphylaxis if they are exposed to the medication. Other risk factors for anaphylaxis include a history of severe allergies, asthma, and a weakened immune system.
- Symptoms of anaphylaxis: The symptoms of anaphylaxis can vary from person to person. However, some of the most common symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, throat, and tongue, hives, itching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness.
- Treatment for anaphylaxis: If you think that you are experiencing anaphylaxis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment for anaphylaxis typically involves epinephrine, which is a medication that can help to open up the airways and reduce swelling. Other medications that may be used to treat anaphylaxis include antihistamines and corticosteroids.
If you have a history of allergies, it is important to talk to your doctor about your risk for anaphylaxis. Your doctor can recommend ways to avoid exposure to allergens and can prescribe epinephrine auto-injectors, which can be used to treat anaphylaxis in an emergency.
4. Diagnosis
Diagnosing an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face involves a combination of evaluating the patient's symptoms and their history of exposure to Neosporin. This approach is crucial because it allows healthcare professionals to accurately identify and differentiate an allergic reaction from other potential causes of facial skin irritation.
- Symptoms: The presence of symptoms such as redness, swelling, itching, burning, and blistering on the face is a key indicator of a possible allergic reaction to Neosporin. These symptoms typically develop within hours or days of exposure to the medication.
- History of exposure: Establishing a history of exposure to Neosporin is essential in making a diagnosis. The patient may have used Neosporin to treat a minor cut, scrape, or burn on their face. It is important to note that even a small amount of Neosporin exposure can trigger an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals.
- Physical examination: During a physical examination, the healthcare professional will assess the affected area on the face, noting the extent and severity of the rash. They may also inquire about any other potential allergens or irritants that the patient has been exposed to.
- Patch testing: In some cases, patch testing may be performed to confirm an allergic reaction to Neosporin. This involves applying a small amount of Neosporin to a patch of skin on the patient's back and monitoring the area for signs of an allergic reaction.
By carefully evaluating the patient's symptoms and history of exposure to Neosporin, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose an allergic reaction and recommend appropriate treatment options. It is important for individuals who suspect they may have an allergic reaction to Neosporin to seek medical attention promptly to avoid potential complications.
5. Prognosis
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can be a distressing experience, but the prognosis for most people is positive. With appropriate treatment, the majority of individuals will make a full recovery and experience a resolution of their symptoms.
- Mild reactions: Mild allergic reactions to Neosporin on the face typically manifest as redness, swelling, itching, and burning. These symptoms usually resolve within a few days with discontinuation of Neosporin use and application of over-the-counter topical antihistamines or calamine lotion.
- Moderate reactions: Moderate allergic reactions may involve more severe symptoms, such as blisters, hives, and difficulty breathing. These reactions require prompt medical attention and may necessitate the use of oral antihistamines, topical or oral corticosteroids, or in severe cases, epinephrine.
- Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis is a rare but life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur within minutes of Neosporin exposure. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and throat, and a rapid pulse. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical intervention and treatment with epinephrine.
- Treatment and recovery: The key to a favorable prognosis for an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face is early recognition and treatment. Discontinuing use of Neosporin and seeking medical attention promptly can help minimize the severity of symptoms and expedite recovery. Avoiding future exposure to Neosporin is crucial to prevent recurrence of allergic reactions.
It is important to note that while most people who experience an allergic reaction to Neosporin will recover with treatment, some individuals may develop chronic skin conditions, such as contact dermatitis, as a result of repeated exposure. Therefore, it is essential to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan and follow the doctor's advice regarding Neosporin use and potential alternatives.
FAQs about Allergic Reaction to Neosporin on Face
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can be a concerning experience. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns and provide essential information:
Question 1: What are the symptoms of an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face?
Allergic reactions to Neosporin on the face can manifest in various ways, including redness, swelling, itching, burning, and blistering. More severe reactions may involve hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face and throat. It is crucial to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any of these symptoms.
Question 2: What causes an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face?
Neosporin contains antibiotics, such as neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin, which can trigger allergic reactions in certain individuals. It is essential to be aware of any allergies you may have before using Neosporin.
Question 3: How is an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face treated?
Treatment for an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face depends on the severity of the reaction. Mild reactions may resolve with discontinuation of Neosporin use and application of topical antihistamines. More severe reactions may require oral antihistamines, topical or oral corticosteroids, or even epinephrine in the case of anaphylaxis.
Question 4: How can I prevent an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face?
The most effective way to prevent an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face is to avoid exposure to the medication. If you have known allergies to any of the components in Neosporin, it is essential to choose alternative treatments for cuts and scrapes.
Question 5: Are there any alternatives to Neosporin for treating minor cuts and scrapes on the face?
Yes, there are several alternative topical antibiotics available for treating minor cuts and scrapes on the face, such as bacitracin or mupirocin. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate option for your specific needs.
Question 6: When should I seek medical attention for an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face?
It is crucial to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any allergic reaction symptoms, especially if they are severe. Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and throat, and hives are all indications of a potentially serious reaction that requires immediate medical intervention.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for an allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can empower you to make informed decisions and seek appropriate medical care when necessary.
Remember, if you have concerns or experience an allergic reaction, it is always advisable to consult a qualified healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Tips to Avoid and Manage Allergic Reactions to Neosporin on the Face
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face can range from mild to severe, and it is essential to take precautions to avoid and manage such reactions effectively.
Tip 1: Identify and Avoid Allergens
The primary step in preventing allergic reactions is to identify and avoid known allergens. If you have experienced an allergic reaction to Neosporin in the past, it is crucial to avoid using it in the future.
Tip 2: Read Ingredient Labels Carefully
Before using any topical medications or products on your face, carefully read the ingredient labels. Neosporin contains three antibiotics: neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin. If you are allergic to any of these ingredients, avoid using Neosporin or products containing these antibiotics.
Tip 3: Perform a Patch Test
If you are unsure whether you are allergic to Neosporin, perform a patch test before applying it to your face. Apply a small amount of Neosporin to a small area of skin on your inner forearm and cover it with a bandage. Leave the patch test on for 24-48 hours and observe the area for any signs of an allergic reaction, such as redness, swelling, or itching.
Tip 4: Use Alternative Treatments
There are several alternative treatments available for minor cuts and scrapes on the face. These include other topical antibiotics, such as bacitracin or mupirocin, as well as over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate alternative treatment for your specific needs.
Tip 5: Seek Medical Attention Promptly
If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction to Neosporin on your face, seek medical attention promptly. Severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, can be life-threatening and require immediate medical intervention.
Summary
By following these tips, you can effectively avoid and manage allergic reactions to Neosporin on the face. Remember to always prioritize your health and safety by taking necessary precautions and seeking medical attention when needed.
Conclusion
An allergic reaction to Neosporin on the face is a prevalent skin condition that can cause discomfort, irritation, and even severe health consequences. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition is crucial for effective management and prevention. This comprehensive exploration of allergic reactions to Neosporin on the face has provided valuable insights into its various aspects, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and prioritize their health.
To reiterate, it is essential to be aware of potential allergies, carefully read ingredient labels, and perform patch tests before using topical medications. Alternative treatments are available for those allergic to Neosporin, and prompt medical attention is necessary for severe reactions. By adhering to these guidelines and seeking professional medical advice when needed, individuals can effectively manage allergic reactions to Neosporin on the face and maintain healthy, well-protected skin.
Article Recommendations
- How To Hire A Hitman Online
- Was Johnny Cashs First Wife Really African American Uncover The Truth
- Clara Babylegs