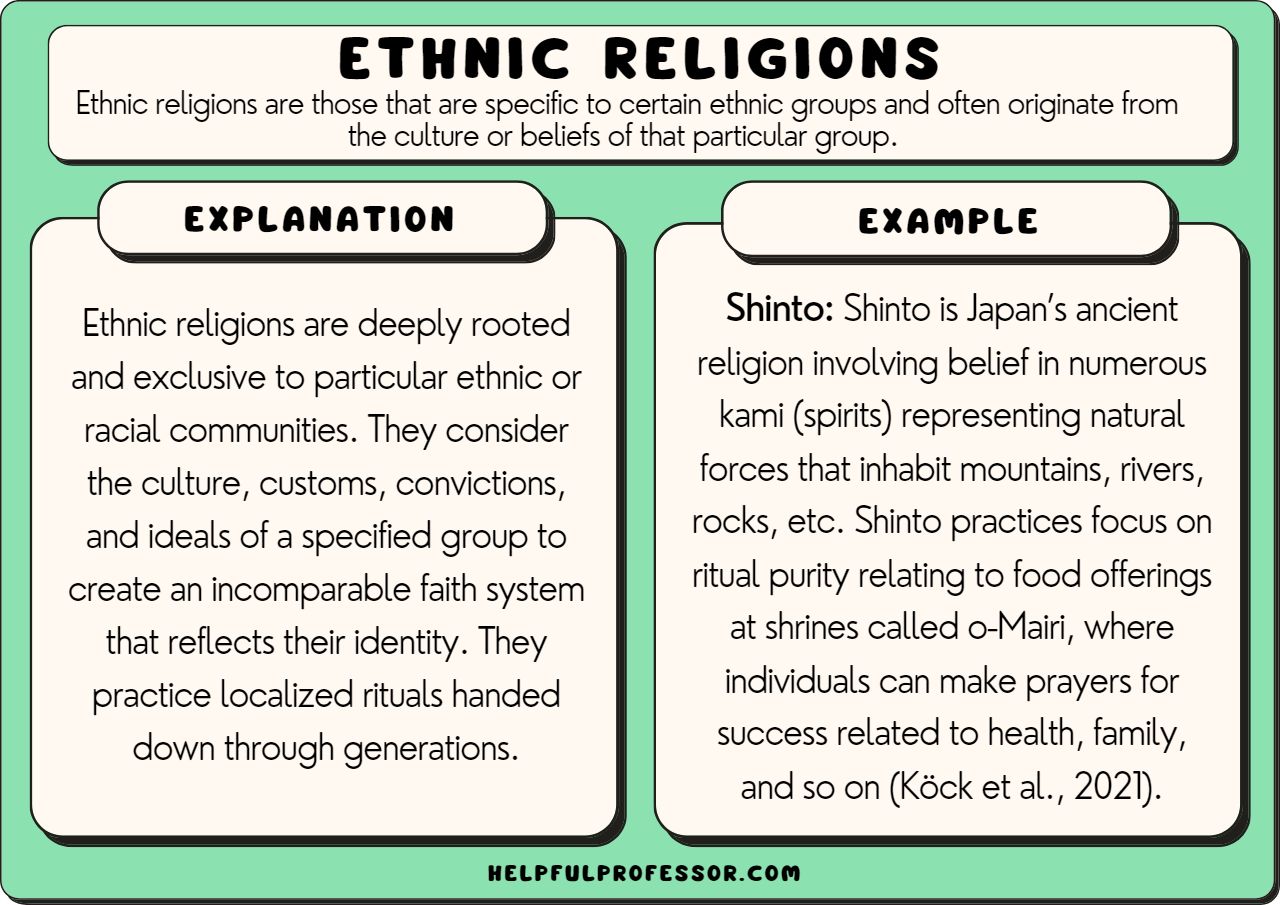
Ethnic religion is a term used to describe religious traditions that are closely tied to a particular ethnic group or culture. Ethnic religions often share a common set of beliefs, practices, and rituals that are passed down from generation to generation. They often play a central role in the cultural identity of the group and may be seen as a way of preserving and transmitting cultural heritage.
Ethnic religions can be found all over the world, and they vary greatly in their specific beliefs and practices. Some common examples of ethnic religions include:
- Hinduism
- Buddhism
- Shinto
- Zoroastrianism
- Judaism
Ethnic religions can be important for a number of reasons. They can provide a sense of belonging and community, and they can help to preserve and transmit cultural heritage. They can also play a role in social and political life, and they can be a source of spiritual and moral guidance.
The study of ethnic religions is a complex and challenging field, but it is also a fascinating one. By studying ethnic religions, we can learn more about the diversity of human religious experience, and we can gain a deeper understanding of the role that religion plays in human culture.
Ethnic Religion Definition
Ethnic religion is a term used to describe religious traditions that are closely tied to a particular ethnic group or culture. Six key aspects of ethnic religion definition are:
- Cultural Identity
- Shared Beliefs
- Common Practices
- Preservation of Heritage
- Sense of Belonging
- Social and Political Role
These aspects are all interconnected and contribute to the unique nature of ethnic religions. For example, the shared beliefs and practices of an ethnic religion can help to create a sense of belonging and community among its members. Additionally, the preservation of cultural heritage through ethnic religion can help to strengthen the identity of the group. Finally, the social and political role of ethnic religion can be significant, as it can provide a source of guidance and support for members of the group.
1. Cultural Identity and Ethnic Religion Definition
Cultural identity is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses an individual's sense of belonging to a particular group or culture. It is shaped by a variety of factors, including ethnicity, race, nationality, religion, and language. In the context of ethnic religion definition, cultural identity plays a central role.
- Shared Values and Beliefs
Ethnic religions often share a common set of values and beliefs that are passed down from generation to generation. These values and beliefs can help to shape the cultural identity of the group and can provide a sense of belonging and community among its members. - Preservation of Heritage
Ethnic religions can also play a role in preserving the cultural heritage of a group. They can provide a means of transmitting cultural traditions, stories, and practices from one generation to the next. This can help to strengthen the cultural identity of the group and ensure that its heritage is not lost. - Sense of Belonging
Ethnic religions can provide a sense of belonging for individuals who may feel marginalized or disconnected from mainstream society. They can offer a sense of community and support, and they can help individuals to connect with their cultural roots. - Social and Political Role
Ethnic religions can also play a significant social and political role in the lives of their adherents. They can provide a source of moral guidance and support, and they can help to shape the political and social values of the group.
In conclusion, cultural identity is a key aspect of ethnic religion definition. The shared values, beliefs, and practices of an ethnic religion can help to shape the cultural identity of the group, preserve its heritage, provide a sense of belonging, and play a significant social and political role.
2. Shared Beliefs and Ethnic Religion Definition
Shared beliefs are a central aspect of ethnic religion definition. They provide a common ground for members of the group and help to shape the group's identity. Shared beliefs can include religious doctrines, moral values, and cultural norms.
- Religious Doctrines
Many ethnic religions have their own unique set of religious doctrines that are shared by members of the group. These doctrines can include beliefs about the nature of the divine, the afterlife, and the moral order. For example, the Yoruba people of Nigeria believe in a pantheon of gods and goddesses, while the Navajo people of the American Southwest believe in a Holy People who created the world.
- Moral Values
Ethnic religions often have their own set of moral values that guide the behavior of members of the group. These values can include virtues such as honesty, compassion, and respect for elders. For example, the Confucian tradition emphasizes the importance of filial piety, while the Sikh tradition emphasizes the importance of equality and service to others.
- Cultural Norms
Ethnic religions can also shape the cultural norms of the group. These norms can include rules about marriage, family life, and. For example, some ethnic religions have rules about who can marry whom, while others have rules about what foods can be eaten. These norms can help to create a sense of community and belonging among members of the group.
In conclusion, shared beliefs are a key aspect of ethnic religion definition. They provide a common ground for members of the group and help to shape the group's identity. These beliefs can include religious doctrines, moral values, and cultural norms.
3. Common Practices
Common practices are an integral part of ethnic religion definition. They are the outward expressions of the group's shared beliefs and values, and they help to create a sense of community and belonging among members of the group.
- Religious Rituals
Many ethnic religions have their own unique set of religious rituals that are performed by members of the group. These rituals can include prayers, sacrifices, and festivals. For example, the Yoruba people of Nigeria have a complex system of religious rituals that are used to honor the gods and goddesses and to ask for their help. These rituals are an important part of Yoruba culture and identity.
- Cultural Celebrations
Ethnic religions often have their own set of cultural celebrations that are held throughout the year. These celebrations can include holidays, festivals, and other special events. For example, the Chinese people celebrate the Lunar New Year with a variety of traditional customs and activities. These celebrations are an important part of Chinese culture and identity.
- Pilgrimages
Many ethnic religions have sacred sites that are visited by pilgrims from all over the world. These sites can include temples, shrines, and other holy places. For example, the Hajj is a pilgrimage to Mecca that is required of all able-bodied Muslims. The Hajj is an important part of Islamic culture and identity.
- Dietary Practices
Some ethnic religions have their own set of dietary practices that are followed by members of the group. These practices can include restrictions on what foods can be eaten, when they can be eaten, and how they can be prepared. For example, the Jewish people have a set of dietary laws that are known as kashrut. Kashrut is an important part of Jewish culture and identity.
Common practices are an important part of ethnic religion definition. They are the outward expressions of the group's shared beliefs and values, and they help to create a sense of community and belonging among members of the group.
4. Preservation of Heritage
The preservation of heritage is a central aspect of ethnic religion definition. Ethnic religions often play a vital role in transmitting cultural traditions, stories, and practices from one generation to the next. This helps to strengthen the cultural identity of the group and ensure that its heritage is not lost.
- Cultural Identity
Ethnic religions can help to preserve the cultural identity of a group by providing a shared set of beliefs, values, and practices. These can include religious rituals, cultural celebrations, and dietary practices. For example, the Jewish people have a set of dietary laws that are known as kashrut. Kashrut is an important part of Jewish culture and identity.
- Cultural Traditions
Ethnic religions can also help to preserve cultural traditions by providing a context for their practice. For example, many Native American tribes have traditional dances and songs that are performed at religious ceremonies. These dances and songs are an important part of Native American culture and identity.
- Cultural Heritage
Ethnic religions can also help to preserve cultural heritage by providing a means of transmitting cultural knowledge from one generation to the next. This can include stories, legends, and myths that are passed down through oral tradition. For example, the Maori people of New Zealand have a rich oral tradition that includes stories about their ancestors, their gods, and their land.
- Cultural Practices
Ethnic religions can also help to preserve cultural practices by providing a context for their performance. For example, many ethnic religions have traditional healing practices that are used to treat illness and disease. These practices are an important part of the cultural heritage of the group.
In conclusion, the preservation of heritage is a key aspect of ethnic religion definition. Ethnic religions play a vital role in transmitting cultural traditions, stories, and practices from one generation to the next. This helps to strengthen the cultural identity of the group and ensure that its heritage is not lost.
5. Sense of Belonging
Within the intricate tapestry of ethnic religion definition, the sense of belonging holds a central thread, weaving together the fabric of community and identity. It is an intrinsic aspect that deeply influences the experiences and practices within ethnic religions.
- Shared Beliefs and Values
Ethnic religions provide a shared framework of beliefs and values that unites members, fostering a profound sense of belonging. These common ground beliefs create a cohesive community where individuals feel connected to something larger than themselves.
- Cultural Practices and Traditions
Ethnic religions are often intertwined with cultural practices and traditions that reinforce a sense of belonging. Participation in rituals, ceremonies, and festivals strengthens the bonds between members and fosters a shared cultural identity.
- Historical and Ancestral Connections
Many ethnic religions have deep historical roots and ancestral connections that create a sense of belonging across generations. Individuals feel a connection to their ancestors and a shared heritage, which contributes to a strong sense of community.
- Social Support and Network
Ethnic religions often provide a network of social support and assistance, particularly in times of need or hardship. This mutual support strengthens the sense of belonging and creates a safety net within the community.
In conclusion, the sense of belonging is an integral part of ethnic religion definition. It encompasses shared beliefs, cultural practices, historical connections, and social support, which collectively create a cohesive community and a deep sense of connectedness among members.
6. Social and Political Role
The social and political role of ethnic religions is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has been studied by scholars for centuries. In this section, we will explore some of the key aspects of this relationship, including the ways in which ethnic religions can shape social and political life, and the ways in which social and political factors can influence the development and practice of ethnic religions.
- Religious Identity and Political Mobilization
Ethnic religions can provide a powerful basis for political mobilization, as they offer a shared sense of identity and purpose to their adherents. This can be seen in the role that religion has played in movements for national liberation, social justice, and political change throughout history. For example, the civil rights movement in the United States was deeply influenced by the African-American church, which provided a source of spiritual and communal support for activists and helped to mobilize the black community.
- Religious Institutions and Social Welfare
Ethnic religions often play a vital role in providing social welfare services to their communities. This can include providing food, shelter, and medical care to the poor and needy, as well as offering educational and vocational training programs. For example, the Catholic Church has a long history of providing social services to the poor and marginalized, and many Buddhist temples in Asia offer educational and vocational training programs to their communities.
- Religious Beliefs and Political Values
The beliefs and values of ethnic religions can have a significant impact on the political values of their adherents. For example, religions that emphasize the importance of compassion and social justice may lead their adherents to support policies that promote these values. Similarly, religions that emphasize the importance of obedience to authority may lead their adherents to support authoritarian political regimes.
- State Regulation of Religion
The relationship between ethnic religions and the state is often complex and contested. In some cases, states have sought to control or suppress ethnic religions, while in other cases they have sought to promote or support them. The policies of the state can have a significant impact on the development and practice of ethnic religions.
In conclusion, the social and political role of ethnic religions is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has been shaped by a variety of historical, cultural, and political factors. The relationship between ethnic religions and the state is often complex and contested, and the policies of the state can have a significant impact on the development and practice of ethnic religions.
FAQs on Ethnic Religion Definition
This section addresses frequently asked questions surrounding ethnic religion definition, clarifying misconceptions and providing a deeper understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What distinguishes ethnic religions from other types of religions?
Ethnic religions are characterized by their close ties to a particular ethnic group or culture. They often share a common set of beliefs, practices, and rituals that are passed down from generation to generation and play a central role in the cultural identity of the group.
Question 2: Are ethnic religions always exclusive and isolated from other belief systems?
Not necessarily. While some ethnic religions may have exclusive beliefs and practices, others are more open and inclusive. Additionally, ethnic religions can interact and influence other belief systems, leading to the exchange of ideas and practices.
Question 3: How do ethnic religions contribute to cultural preservation?
Ethnic religions often serve as guardians of cultural heritage, preserving traditions, stories, and practices that are unique to the ethnic group. By transmitting cultural knowledge to future generations, they help maintain the group's cultural identity and sense of continuity.
Question 4: Can ethnic religions have a political or social impact?
Yes, ethnic religions can play a significant role in social and political life. They can provide a sense of community, shape moral values, and influence political ideologies. Additionally, ethnic religious leaders may engage in political activism or provide guidance on social issues.
Question 5: Is it appropriate to study and research ethnic religions from an academic perspective?
Absolutely. Studying ethnic religions from an academic perspective allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of diverse belief systems, cultural practices, and their impact on society. This knowledge contributes to a broader understanding of human religious expression and cultural diversity.
Question 6: How can we promote respect and understanding of ethnic religions?
Respecting ethnic religions involves recognizing the validity and significance of different belief systems. It requires open-mindedness, empathy, and a willingness to learn about and engage with religious practices that may differ from our own.
In conclusion, ethnic religion definition encompasses a diverse range of religious traditions closely intertwined with ethnic identity and cultural heritage. These religions contribute to cultural preservation, shape social and political values, and provide a sense of community. Understanding and respecting ethnic religions is essential for fostering interfaith dialogue and promoting cultural diversity.
Moving forward, we will delve into the significance of rituals and symbols in ethnic religions, exploring their functions and meanings.
Understanding Ethnic Religion Definitions
Comprehending ethnic religion definitions is crucial for appreciating the diversity of religious expression and its significance in cultural identity. Here are some tips to enhance your understanding:
Tip 1: Recognize the Cultural Context
Ethnic religions are deeply rooted in specific cultures and ethnic groups. Understanding the cultural context, including historical, linguistic, and social factors, provides a foundation for grasping the nuances of ethnic religious beliefs and practices.
Tip 2: Focus on Shared Characteristics
Ethnic religions often share common characteristics, such as a shared mythology, rituals, and moral values. Identifying these shared elements helps define the unique features of each ethnic religion and distinguish it from other belief systems.
Tip 3: Examine the Role of Tradition
Tradition plays a vital role in ethnic religions. Beliefs and practices are often passed down through generations, shaping the identity and continuity of the religious community. Understanding the significance of tradition provides insights into the stability and adaptability of ethnic religions.
Tip 4: Consider the Social and Political Dimensions
Ethnic religions can have significant social and political implications. They may influence social structures, ethical norms, and political ideologies. Recognizing these dimensions helps comprehend the broader impact of ethnic religions on society.
Tip 5: Respect Diversity and Avoid Stereotypes
Ethnic religions exhibit immense diversity, and it is crucial to avoid generalizations or stereotypes. Each ethnic religion has its unique characteristics and should be approached with respect and openness.
By following these tips, you can deepen your understanding of ethnic religion definitions and appreciate their significance in shaping cultural and religious landscapes.
Conclusion:
Comprehending ethnic religion definitions is essential for fostering interfaith understanding and preserving cultural heritage. By embracing these tips, you can embark on a journey of discovery, gaining a nuanced appreciation for the rich tapestry of religious traditions that enrich human existence.
Conclusion
This exploration of ethnic religion definition has highlighted the intricate relationship between culture, identity, and religious expression. Ethnic religions are not merely belief systems but integral parts of cultural heritage, shaping communities and providing a profound sense of belonging.
Understanding ethnic religion definitions is not only an academic pursuit but also a path toward fostering interfaith dialogue and promoting cultural diversity. By recognizing the unique characteristics and contributions of ethnic religions, we enrich our collective understanding of human spirituality and cultural expression.
Article Recommendations
- Stream Smarter With Tvyoutube Start Your Tv Journey Today
- Discover Trs Your Safe Haven For Detoxing Heavy Metals
- Lifetouch Customer Service